문제
우리 나라는 가족 혹은 친척들 사이의 관계를 촌수라는 단위로 표현하는 독특한 문화를 가지고 있다. 이러한 촌수는 다음과 같은 방식으로 계산된다. 기본적으로 부모와 자식 사이를 1촌으로 정의하고 이로부터 사람들 간의 촌수를 계산한다. 예를 들면 나와 아버지, 아버지와 할아버지는 각각 1촌으로 나와 할아버지는 2촌이 되고, 아버지 형제들과 할아버지는 1촌, 나와 아버지 형제들과는 3촌이 된다.
여러 사람들에 대한 부모 자식들 간의 관계가 주어졌을 때, 주어진 두 사람의 촌수를 계산하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
사람들은 1, 2, 3, …, n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100)의 연속된 번호로 각각 표시된다. 입력 파일의 첫째 줄에는 전체 사람의 수 n이 주어지고, 둘째 줄에는 촌수를 계산해야 하는 서로 다른 두 사람의 번호가 주어진다. 그리고 셋째 줄에는 부모 자식들 간의 관계의 개수 m이 주어진다. 넷째 줄부터는 부모 자식간의 관계를 나타내는 두 번호 x,y가 각 줄에 나온다. 이때 앞에 나오는 번호 x는 뒤에 나오는 정수 y의 부모 번호를 나타낸다.
각 사람의 부모는 최대 한 명만 주어진다.
출력
입력에서 요구한 두 사람의 촌수를 나타내는 정수를 출력한다. 어떤 경우에는 두 사람의 친척 관계가 전혀 없어 촌수를 계산할 수 없을 때가 있다. 이때에는 -1을 출력해야 한다.
예제 입출력
풀이 - 정석적인 정답
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class Person{
int number, degreeOfKinship;
Person(int number, int degreeOfKinship){
this.number = number;
this.degreeOfKinship = degreeOfKinship;
}
}
public class Main {
static int n, m, person1, person2;
static List<List<Person>> map;
static int countOfMatch, answer;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
n = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine()); //전체 사람 수
map = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { //전체 사람 수만큼 ArrayList 공간 할당
map.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
person1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //촌수를 구해야 할 사람 2명
person2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine()); //부모-자식 관계 개수
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int parent = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //부모
int child = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //자식
map.get(parent).add(new Person(child, 0)); //촌수 값 0 기본 세팅
map.get(child).add(new Person(parent, 0));
}
System.out.println(BFS(person1, person2));
}
public static int BFS(int start, int end){
Queue<Person> Q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visit = new boolean[n+1];
Q.add(new Person(start, 0));
visit[start]=true;
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
Person nowPerson = Q.poll();
if(nowPerson.number==end) return nowPerson.degreeOfKinship;
for(Person nxtPerson : map.get(nowPerson.number)){
if(!visit[nxtPerson.number]) {
visit[nxtPerson.number]=true;
//촌수 계산
nxtPerson.degreeOfKinship = nowPerson.degreeOfKinship+1;
Q.add(nxtPerson);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
풀이2 - 푸는 중
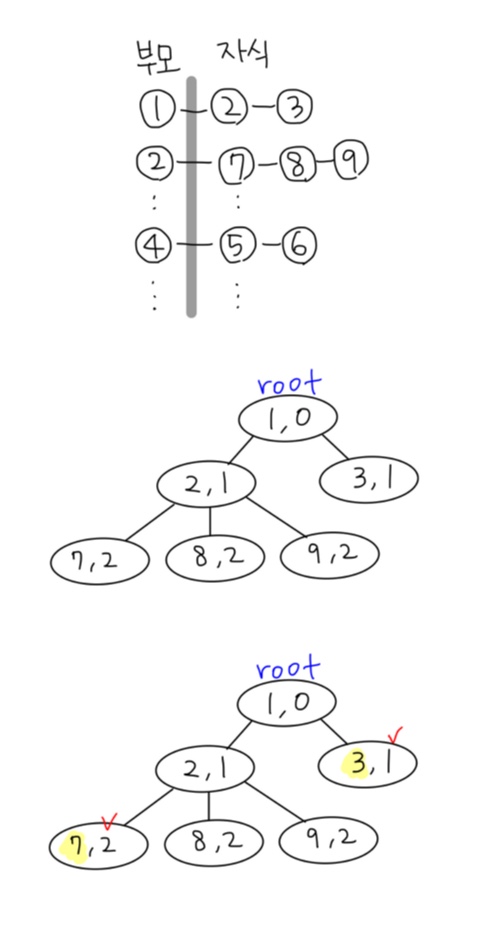
root 노드인 1부터 차례대로 다른 노드의 depth 값을 구한다.
노드1과 노드2의 촌수 값은 root~노드1 depth + root~노드2 depth 값이라고 두고 풀어봤다.
부모-자식 쌍으로 번호가 주어지고, 각 사람의 부모는 최대 한 명만 주어지기 때문에
양방향 연결성을 고려하지 않아도 풀이가 가능할 것이라고 생각했다.
그렇지만 뭐가 문제징 ? ? ? ? ? ? 해결하는 중이다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class Person{
int number, degreeOfKinship;
Person(int number, int degreeOfKinship){
this.number = number;
this.degreeOfKinship = degreeOfKinship;
}
}
public class Main {
static int m, person1, person2;
static List<List<Person>> map;
static int countOfMatch, answer;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int n = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine()); //전체 사람 수
map = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { //전체 사람 수만큼 ArrayList 공간 할당
map.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
person1 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //촌수를 구해야 할 사람 2명
person2 = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine()); //부모-자식 관계 개수
// 이때 앞에 나오는 번호 x는 뒤에 나오는 정수 y의 부모 번호를 나타낸다.
// 각 사람의 부모는 최대 한 명만 주어진다.
// 부모-자식 한 번만 연결해서 풀 수는 없을까?
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int parent = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //부모
int child = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //자식
map.get(parent).add(new Person(child, 0)); //촌수 값 0 기본 세팅
}
System.out.println(BFS(1));
}
public static int BFS(int root){
Queue<Person> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.add(new Person(root, 0));
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
Person parent = Q.poll();
for(Person child : map.get(parent.number)) {
//자식의 depth = 부모 depth+1
child.degreeOfKinship = parent.degreeOfKinship+1;
//자식이 촌수를 구해야 할 사람에 포함되면 체크
if(child.number==person1 || child.number==person2) {
countOfMatch++;
answer += child.degreeOfKinship;
}
if(countOfMatch==2) return answer;
Q.add(child);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
'Algorithm > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준/JAVA] 🥈 16953번 A → B (0) | 2023.12.15 |
|---|---|
| [백준/JAVA] 🥈 15650번 N과 M (2) (0) | 2023.12.14 |
| [백준/JAVA] 🥈 7562번 나이트의 이동 (1) | 2023.12.10 |
| [백준/JAVA] 🥈 2667번 단지번호붙이기 (1) | 2023.12.06 |
| [백준/JAVA] 🥈 2178번 미로 탐색 (1) | 2023.12.06 |



